Cataract Management
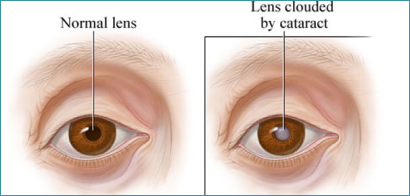
What is Cataract ?
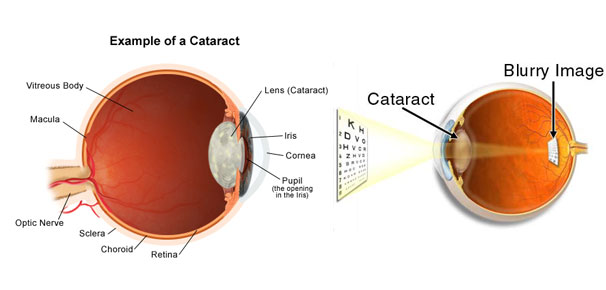
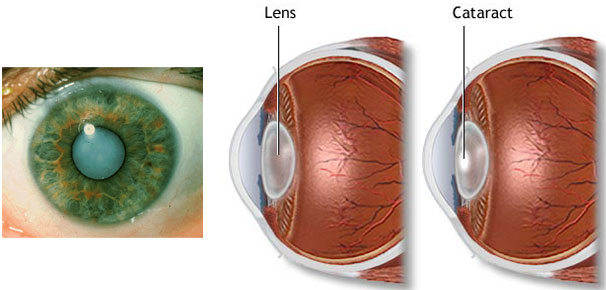
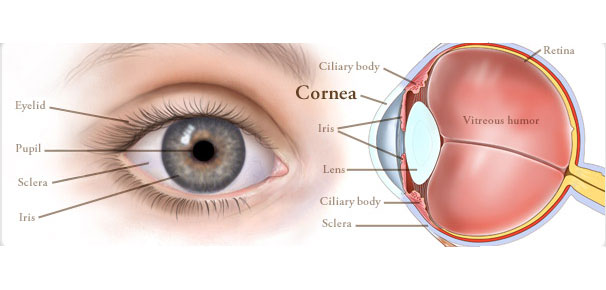
In the normal eye the lens inside is clear and transparent, but when cataract develops it becomes cloudy and opaque. So the light is not focused on the retina through lens which leads to blurring of vision.
How Cataract develops ?
Cataract can be developed with age (Senile Cataract) Child can be born with cataract (Congenital Cataract) X-ray & other radiation (UV light) can cause cataract (Radiation Cataract) Exposure to sunlight, Diabetes and Heredity are also factors for the Cataract development.
What are the Symptoms of Cataract ?
As mentioned, it is related. Blurred vision worsens with time. Some complains about dimness in eye and brightness in the other eye. Printed images may seem distorted. Glaring effect may be experienced. However, Cataract never causes pain, itching or redness.
Can Cataract be prevented ?
No, till date no preventive measure is found for the Cataract. It is an age related changes. No drugs, diets or medicine can delay or cure the Cataract. However, Wearing a sunglass that blocks the UV rays can slow down the process of development of Cataract.
What are the Symptoms of Cataract ?
As mentioned, it is related. Blurred vision worsens with time. Some complains about dimness in eye and brightness in the other eye. Printed images may seem distorted. Glaring effect may be experienced. However, Cataract never causes pain, itching or redness.
Can Cataract be prevented ?
No, till date no preventive measure is found for the Cataract. It is an age related changes. No drugs, diets or medicine can delay or cure the Cataract. However, Wearing a sunglass that blocks the UV rays can slow down the process of development of Cataract.
How Cataract is treated ?
Surgery is the only way to remove the Cataract.
What exactly done in Cataract Surgery ?
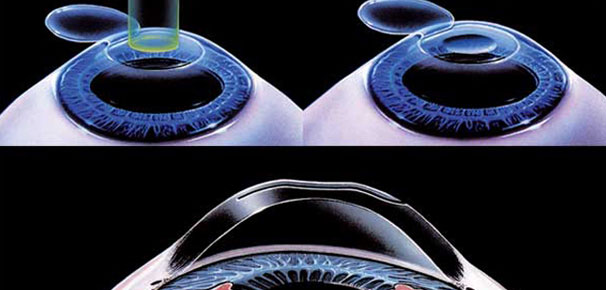
Under an operating microscope and with Phaco-emulsification machine a small cut is made in the eye and cloudy lens is removed and plastic Intra-ocular Lens is placed in place of natural lens.
Will Surgery improve the vision ?
Over 95% of Cataract surgery will improve the vision. While pre-existing associated condition like glaucoma, diabetes, retinal condition etc may limit the vision even after surgery. Yet, Cataract surgery may still be worthwhile and necessary.
When should I Plan my surgery ?
Under ordinary circumstances cataract surgery is not an emergency situation except few rare instances. Therefore in most of the cases the choice of undergoing surgery largely depends upon patients. In the past, surgeons usually waited till the time Cataract becomes mature or ripe, but modern technique an advances have now made possible to perform Cataract removal at early stage. When it interferes with your day to day work, it is time for surgery. However, it is advisable to have cataract operated early before it becomes hard. An Ophthalmologist can give proper guidance.
What are the surgical techniques ?
In recent time, two techniques are widely performed like;
ECCE ( Extra Capsular Cataract Extraction): It is safe and perform under the operating microscope where the posterior (back membrane) of Cataract is kept inside purposefully to support the IOL (Intra Ocular Lens). The big incision of around 8-10 mm is sutured with very thin thread.
PE (Phaco Emulsification): It is the latest technique which is performed by computerized machine. Since incision is very small of 2.85 mm, no sutures are required and rehabilitation of the patient is quick and fast.
Comparison of these two techniques
| Phaco-emulsification | ECCE | |
| Incision | 3 mm | 8-10 mm |
| Sutures | No Sutures | 6-7 sutures |
| Healing Period | 10-15 Days | 50-60 Days |
| Operation Time | 10 to 15 min. | 30-40 min |
| Technique | Computerized | Manual |
| IOL Foldable | Silicone IOL | Acrylic |
| Post operative Astigmatism | Very less | Can be more |
Which technique is preferred ?
Phaco-emulsification will be the best of choice, however Ophthalmologist will be able to guide you more regarding this.
How long one has to stay in the Hospital after the surgery ?
It is Out Patient Surgery, no stay is required. Patient will be discharged immediately after the surgery.
What post operative care is required ?
After surgery you should be able to resume most activities almost immediately. You will be cautioned against heavy lifting and strenuous exercise to avoid putting unnecessary strain on the tiny structures as your eye heals.
What about gaining of normal vision ?
Vision usually improve within a few days after surgery, but complete healing of the eye takes about a month. Vision continues to improve as the eye heals.
What is After-Cataract Yag Laser Treatment ?
Since the posterior (back) portion of the lens capsule is left inside the eye purposefully to support the IOL (Intra Ocular Lens). Over a period of time, the cells of the capsule grow and make the capsule thick and opaque which obscure the vision. This is not the complication. With help of the Yag Laser small opening is made in the capsule just in few seconds without the surgery. Yag Laser Treatment is noninvasive OPD procedures, requires no anesthesia and no patch. Younger patients are more prone of thickening of Capsule.
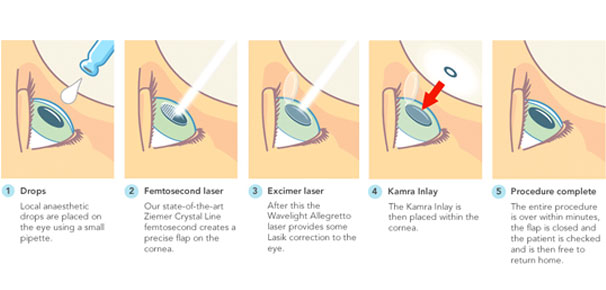
Bladeless & Conventional Lasik Procedure
LASIK
Can anybody have laser surgery?
Most patients are very pleased with the results of their refractive surgery. However, like any other medical procedure, there are risks involved. That’s why it is important for you to understand the limitations and possible complications of refractive surgery.
In order to asses whether your refractive error qualifies for this type of correction, it is important to obtain your
complete medical history and to have a detailed eye exam performed by the ophthalmologist.
In general:
Your refractive error should be stable.
You should be at least 18 years old.
You should have no ophthalmologic disorders (such as cataract or glaucoma) should be present.You should be free of certain general illnesses as they may interfere with the healing process.You should not be taking any medication which may have an effect on the healing process of the cornea.
You should not be pregnant or breastfeeding.
If you suffer from seasonal allergies, surgery should be scheduled at an allergy-free time.
Can children have laser surgery?
We do not recommend treating children’s refractive errors with eye laser surgery. Because the eye does not stop growing until after the end of puberty (approximately age 20), corrections made before then will not produce stable results. Multiple corrective surgeries would become necessary and preoperative conditions would become more and more complicated. This may cause permanent damage to the cornea and, in extreme cases, require a corneal transplant.
What is the difference between the standard LASIK, and computer-guided or “customized” LASIK?
The actual surgery is the same for all 3 LASIK procedures. The difference is in the measurement of refractive errors prior to surgery.
Standard LASIKIn the standard LASIK procedure, the targeted change in the refractive power of the cornea is based on subjective refraction – a determination of the refractive error by the patient’s choice of corrective lenses during the pre-operative eye examination.
Topolink LASIK or customized ablation
This LASIK procedure the targeted change is based on a combination of subjective refraction and a topographic image of the corneal surface. The goal is to optimize visual correction by eliminating corneal irregularities.
Wavefront LASIK
A Wavefront or Aberrometer-guided LASIK procedure aims to correct the combined refractive error resulting from the optical system of the eye as a whole: the cornea, the lens and the vitreous body.
Femto-LASIK:
Precision, Safety and Superior Results
Complications arising from LASIK surgery, while relatively rare, are usually associated with the oscillating blade on traditional hand-held microkeratomes. Metal blades might create incomplete or uneven edges on the corneal flap, resulting in an abnormal corneal surface and vision defects such as irregular astigmatism. In contrast, the femtosecond laser produces a flap of precise size, shape and depth.
What are the risk & complications following lasik?
Severe pain or sudden decrease in vision should not occur.
If you experience these symptoms, please contact our medical hotline immediately and you will receive strict instructions from a physician.
The following complications may occure in less than 1% of LASIK patients:
Flap complications
To ensure optimal treatment, we follow international guidelines that have been established for the LASIK procedure. They concern the thickness of the corneal flap (160 to 180 micrometer), the thickness of the remaining corneal tissue in the stromal bed (250 micrometer) and the size of the treatment area (6.0 to 6.5 millimeter).
In step one of LASIK surgery a small incision is made to create the corneal flap. In the unlikely event that the incision is irregular or incomplete, we will terminate the surgery, and the procedure can be repeated after 6 months. If, however, the tissue for the corneal flap is separated completely, laser ablation (step-two) can still take place. The area where the flap is made will have been marked prior to surgery and can therefore be placed back into its exact position without difficulty. You will then receive a therapeutic contact lens to prevent the flap from moving.
Over- or undercorrection
In some cases, an overcorrection or undercorrection amounting to approximately 10% – 20% of the desired result is possible. This is usually the result of individual variations in tissue property or in the healing process. In most cases, an enhancement procedure (follow-up surgery) can then be performed approximately 6 months after the initial surgery.
Decentralized optical zone
In rare cases, the treatment zone may become decentralized, which would also necessitate an enhancement procedure (follow-up surgery).
Epithelial ingrowth
During the initial recovery period, it is possible that cells of the epithelium (the outer layer of the cornea) could migrate between the corneal flap and the stromal bed, where they may start growing. In order to avoid any adverse effect on your vision, the flap will then be lifted, so that these cells can be removed.
InfectionIn order to avoid an eye infection, you will receive antibiotic eye drops during and after the surgery. In case you experience any severe pain, or if an eye infection develops even in spite of all precautionary measures, please contact our medical hotline immediately and observe all instructions given by the physician.
Halos and Glare
After surgery, some patients have reported seeing a “halo” or glare around light sources. These effects are subject to the individual healing process and will disappear after a few weeks.
Re-LASIKThe chances of needing an enhancement procedure (follow-up surgery) to obtain the desired correction result is very low – the risk of the patient’s vision being worse after surgery than it was before is statistically less than 1%.
The risk of becoming blind
after surgery is extremely low but, as with any medical procedure, we cannot provide a 100% guarantee. You can be assured that we will do everything we can to protect your health and safety. You can talk to any of our staff member about your concerns. Your surgeon will counsel you on all possible risks.
Advantages of the Femto-LASIK and traditional LASIK
Method of Choice
LASIK can be used to correct 90 % of all refractive errors. This procedure is recommended for the treatment of nearsightedness up to -10 diopter, farsightedness up to +3 diopter and astigmatism up to 3 diopter.
Innovative, Technically Precise ProcedureLASIK is an innovative, technically mature surgical procedure. The use of computer-guided equipment, such as the microkeratome, femtosecond laser and the excimer laser, guarantees predictably accurate results.
Fast and Painless ProcedureLASIK surgery is quick, usually painless and has no effect on your general health. You begin the brief recovery at home directly after the surgery is performed.
Fast Visual RecoveryA few hours after surgery, you will begin regain your vision. The rehabilitation period is very short. Within 2 days, you should be able to continue your daily routines and start to enjoy life without the need for corrective lens.
Fast Wound Healing Without ComplicationsLASIK surgery utilizes the body’s own healing process. In the first step of LASIK surgery, a flap is created on the top surface of the cornea and is turned over like the cover of a book. After completion of the procedure on the underlying stromal bed of the cornea (second step), the flap is positioned back onto the treated area and serves as the body’s own protective band-aid.
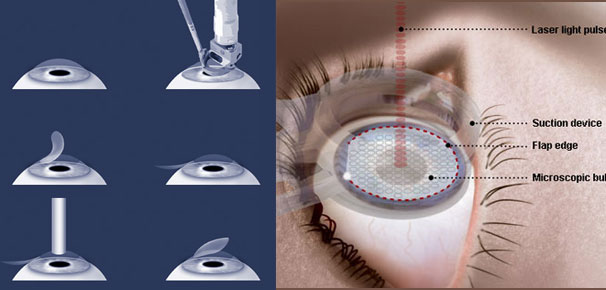
The Femto-LASIK (Laser LASIK) Procedure
The femtosecond laser eliminates the need to use a blade at all. The computer-controlled laser technology works by delivering rapid pulses of light, a quadrillionth of a second each, to a pre-programmed depth and position within the cornea.
Step 1: Preparation of the corneal flap with the femtosecond laser
The LASIK surgeon uses computer software to guide the laser beam. The surgeon can define the diameter and depth of the flap precisely.
The femtosecond laser uses a low vacuum suction ring to hold the eye. Microkeratomes require a higher vacuum suction ring.
The laser inserts a series of tiny (3-micron-diameter) bubbles within the central layer of the cornea. As the femtosecond laser moves back and forth across the eye, the bubbles are connected so they form a corneal flap.
The surgeon can follow the progress through the operating microscope and on a special monitor. A small section of tissue at one edge of the flap is left uncut, forming a hinge that allows the surgeon to fold back the flap so that the cornea can be accessed and reshaped for vision correction. After the flap is finished, the doctor gently lifts the flap.
Step 2: Vision correction with the excimer laser
Now, the excimer laser is used to reshape the cornea in order to correct the refractive error.
Finally, the corneal flap is replaced and functions as a natural band aid.
ICL implantation for high Myopia
An Excellent Vision Correction Option
The ICL (Implantable Contact Lens) is a state-of-art refractive error solution that is ideal for anyone who has the need or desire for removal of power with high quality of vision correction. ICL or Implantable Contact Lens, as the name suggests, is a kind of lens which is implanted into the eye and does not require frequent removal like a normal contact lens. This phakic intraocular lens has numerous advantages including its correction of the widest range of myopia (near sightedness), hyperopia (far sightedness) and astigmatism (cylindrical power).
– ICL can correct a wide range of vision errors by permanently inserting a Contact Lens in front of the natural lens of the eye.
– ICL can correct a wide range of vision errors by permanently inserting a Contact Lens in front of the natural lens of the eye.
– ICL is a kind of soft contact lens which is inserted into the eye through a very small incision.
– Just like LASIK it takes only 5-10 minutes for the procedure. The lens is customize according to each eye’s shape and size.
– Widest power correction range from + 10D to – 20D with cylinder upto 6D
– Made from a material called “Collamer” which is bio compatible ( safe to stay in the eye for very long time).
– This new technique is similar to cataract surgery, but the natural lens remains in place so the eye’s natural focusing ability is preserved.
– An implantable contact lens is beneficial because it becomes a permanent fixture of the eye, avoiding time consuming maintenance.
– It does not get lost, or have to be replaced like glasses and contact lenses.
– ICL procedures are being used on highly nearsighted and farsighted patients who may not be candidates for the more common laser procedures such as LASIK, LASEK and PRK. Unlike laser vision correction procedures that permanently change your vision, it is possible to later remove an ICL .
How do I know if I am a suitable ICL candidate?
1. Candidates for the ICL are above 18 years of age, suffer from myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness) and/or astigmatism (Cylindrical power) and want to experience superior vision correction.
2. Candidate with refractive error who are unsuitable for laser refractive surgery.
3. Prospective person should consult his/her ophthalmologist (eye surgeon) for more information, including an assessment of their candidacy.
4. Women who are pregnant or nursing should wait to have the ICL implanted.
5. Lastly, those without a large enough anterior chamber depth or endothelial cell density may not be a good ICL candidate.
Advantages of ICL
No blood! No pain! No hospitalisation!
Almost all levels of power can be treated.
Excellent quality of vision.
Easily removed or replaced ( 5 – 10 minutes)
Cosmetically good as it’s INVISIBLE!!
Fast recovery
Why Patients Seek ICL
High quality of vision : The ICL not only corrects your refractive power or number, but it also enhances your quality of vision by producing sharp vision.
Wide Treatment Range : In comparison to other refractive procedures, the ICL offers the widest treatment range for correction of vision.
Foldable : Because the ICL is foldable, a small incision is required during the procedure. This feature makes the procedure efficient (no sutures needed) and improves healing time.
Invisible : The placement of the ICL into the posterior chamber of the eye makes the lens invisible to both the patient and any observer.
Collamer Composition : Collamer is made from collagen, which is a substance that naturally occurs in the body. This makes the lens highly biocompatible with the eye.
Proven Track Record : Implated in over 65,000 eyes worldwide, the safety and amazing improvement in vision quality of the ICL has been proven over the last 5 years.
How does the ICL work?
Similar to a contact lens
Designed to remain inside the eye
Doesn’t get dirty and needs no maintenance unlike a contact lens
Once -a- year visit to hospital recommended for examination
How does the ICL differ from other refractive procedures?
Does not cut or remove tissue from the cornea
Cornea retains it natural shape
Safer for higher degrees of myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism and thin corneas.
Less glare issues on patients with large pupils.
Very stable overtime, no regression
What to expect on the procedure?
Procedure should take 10-15 minutes per eye
Laser Iridotomies done prior to surgery
Dilating and anesthetic drops
The ICL Procedure
The implant surgery is quick and painless, lasting only about 10-15 minutes. The area around your eyes will be cleaned and a sterile drape may be applied around your eye.
Eye drops or a local anesthetic will be used to numb your eyes.
When your eye is completely numb, an eyelid speculum will be placed between your eyelids to keep you from blinking during the procedure.
The recovery time is short and the results of the surgery are almost immediate.
Most patients resume normal activities within a week
Potential ICL risks include
Overcorrection : This complication occurs if the prescriptive power of the implanted ICL is too strong. In most cases it can be corrected with corrective eyewear or with an ICL replacement.
Undercorrection : The opposite of overcorrection, undercorrection is the result of an implantable contact lens with too weak of a prescription. Correction methods are similar to those of overcorrection.
Infection : During most surgeries, there is a potential risk of an infection.
Increased intraocular pressure : Pressure may build in the eye after an ICL procedure. The sooner a surgeon is alerted to this, the greater the chance of avoiding serious damage.
This is detected during your follow up visits with us or in case you face acute blurring of vision or headaches, you must visit the eye clinic. ICL may rarely need to be repositioned.
Damage to crystalline lens : because implantable contact lenses are implanted into the eye, there is a potential that the eye’s natural lens may be damaged during the procedure. If the damage is severe, the crystalline lens may need to be replaced with an intraocular lens.
Cataract development : Over 50 percent of the population will develop cataracts by the age of 65, however, it is believed that the use of some implantable contact lenses may cause cataracts at an earlier age, this however is rare.
Halos, glare, and double vision : Updated ICL models greatly diminish the risks of halos, glare, and double vision.
Retinal detachment : Less than 1 percent of patients in the clinical studies were affected by retinal detachment. It should be noted, however, that the occurrence of retinal detachment increased as the degree of myopia increased.
Medical Retina
What is Retina ?
It is the innermost layer of the eye responsible for vision.
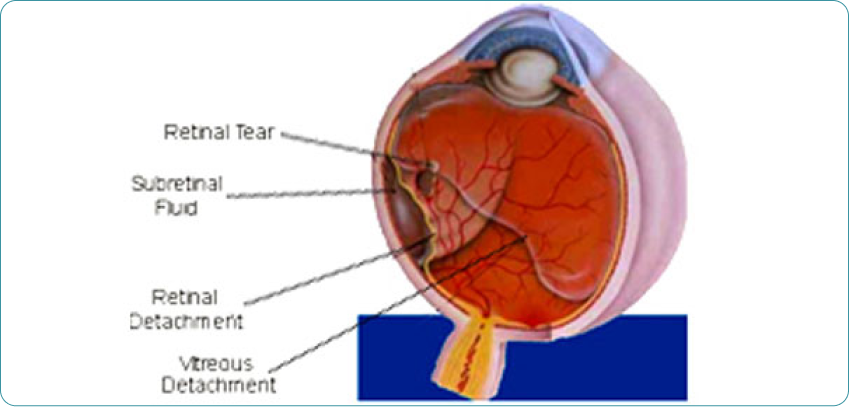
What is Retinal Detachment? (R.D)
It is the separation of retina from the other layers of eye.
Who are at Risk ?
Patients with family history of Retinal Detachment
Patients with high minus power (MYOPES)
Patients with presence of holes/tears in their Retina
Patients with advanced Diabetes Mellitus
Any injury to the eye
Preterm babies
Birth defects in the Retina
Following inflammation/infection of the eye
Tumours affecting the inner layer of the eye
Retina
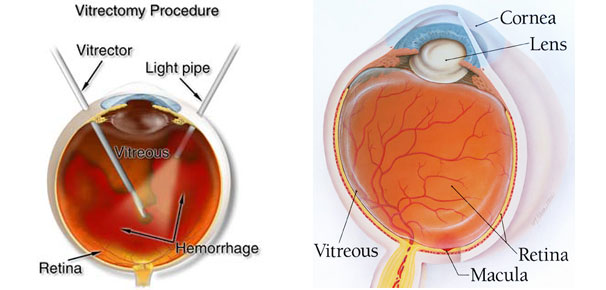
What is retina and vitreous?
The eye functions like a camera the structures such as the cornea and lens focus the light on to the retina; the pupil acts like a camera diaphragm, regulating the amount of light that enters the eye.
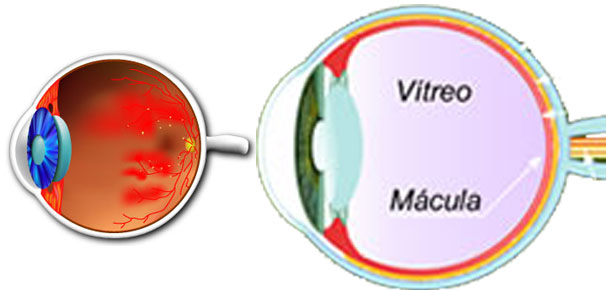
The retina is the light sensitive tissue that lines the inner wall of the eye. The retina converts the visual image in to a signal that the brain can interpret. This signal is transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve. The retina is akin to the film in the camera. However expensive the camera may be, if the film is defective, one doesn’t get good photos. Similarly if the retina is affected, we don’t see well.
The central retina, called the “macula” is the most sensitive part. If we are able enjoy reading, recognize people we love, marvel at the intricate designs on a carving, it is because of the macula. If the macula is affected by disease we may lose some of these capabilities
Why retinal examination is important?
Retina is an extension of the brain. Much like the brain tissue, retina cannot regenerate diseases of the vitreous and retina can cause permanent blindness. Prompt and appropriate treatment can halt further damage and result in better outcome. Retinal examination allows early detection and treatment of retinal disorders.
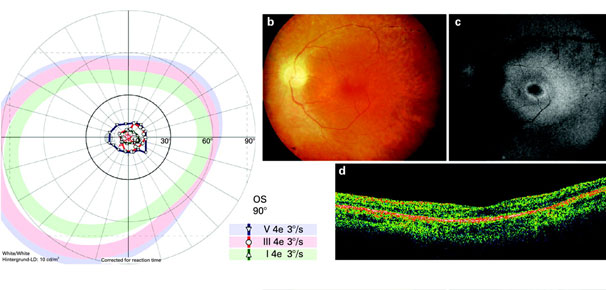
What are the commonly advised investigations by a retinal specialist?
Retinal Angiogram (FFA & ICG)
Ultrasound scan (B-scan)
Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
What is FFA test?
FFA stands for fundus fluorescein angiography. This is a special test to evaluate the structure and health of the blood vessels within the retina by injecting a special dye in to a vein. This valuable test helps your doctor make the correct diagnosis and plan the best course of treatment. If you are diagnosed to have diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration or retinal blood vessel occlusion, you may be advised the test.
What is Ultrasonography (B scan)?
This is a painless test that makes use of sound waves to image the inside of the eye if the inside of the eye cannot be seen using routine clinical methods.
What is OCT?
OCT gives a cross-section view of the retina. Swelling of the retina, collection of fluid beneath the retina, anomalous blood vessels can be seen well with this test.
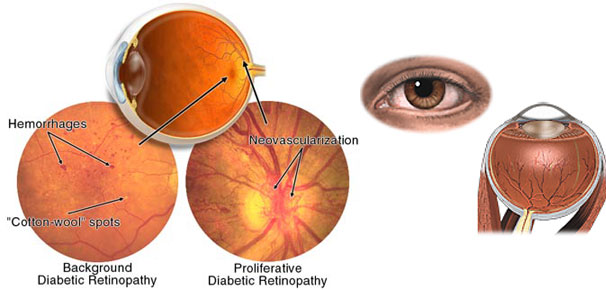
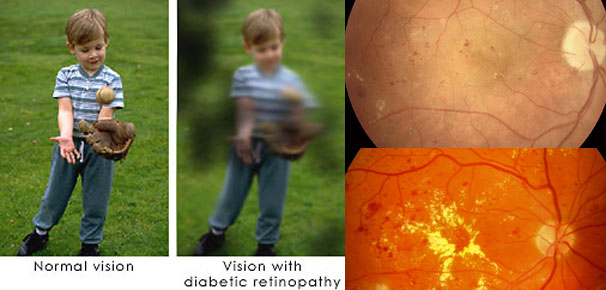
How does Diabetes affect the retina?
Diabetes affects the tiny blood vessels called capillaries of many organs, notably the retina, kidneys and nerve tissue. Diabetes affecting the retina is called Diabetic Retinopathy
The damaged capillaries in the retina leak blood, fluid, and proteins in to the retina resulting in retinal edema. When the edema involves the central retina (Macula), vision may be affected because of Macular Edema.
Further damage to retinal capillaries results in capillary closure and large part of the retina loses its blood supply and becomes ischemic. The ischemic retina manufactures new blood vessels in an attempt to revascularize itself. However, these new blood vessels are very friable and can rupture easily leading to bleeding within the eye.
When bleeding occurs, you will notice black spots swimming across your vision and if bleeding is large, you may lose vision. Over time, scar tissue proliferates within the eye, pulling the retina away from the underlying structures resulting in “Retinal Detachment”. You may lose vision once this occurs.
Longer the duration of diabetes, more are the chances of vision being affected Macular edema (central retinal swelling), bleeding in to the cavity of the eye and retinal detachment can all result in vision loss in diabetics
What should a diabetic do to prevent damage to the retina?
Very good control of blood sugar
Keep blood pressure, cholesterol under control
Check for kidney disease and keep it under control
If you are anemic, take treatment for the same
Can Diabetes affect other parts of the eye?
Diabetes can also cause cataract, weakness of the optic nerve or eye muscles or increase in eye pressure. Cataracts occur at a younger age in diabetic patients. Damage to the small vessels of the optic nerve can affect vision, and weakness of the eye muscles may cause double vision.
A diabetic is also more likely to develop sudden loss of vision due to occlusion of the retinal vessels (branch or central retinal vein occlusion), bleeding in the vitreous cavity, detachment of the retina, or infections.
How is Diabetic Retinopathy treated?
Macular edema (swelling of the central retina) is usually treated with LASER therapy. Some forms of macular edema may be treated with special injections in to the eye. More than one session of LASER therapy may at times be necessary.
When the disease reaches the stage of new blood vessel growth, 3 to 4 sessions of LASER therapy spread out over a week or so may be necessary. If the disease does not come under control, additional sessions of LASER may be needed.
LASER can be performed only before bleeding occurs. Once bleeding has already occurred, LASER may be difficult or impossible.
Severe bleeding or retinal detachment will require microsurgery (vitreous surgery) to restore some vision.
What to expect during LASER therapy?
LASER is using a special form of light to destroy areas of abnormal retina.
Your pupils will be dilated first and then the eye will be anesthetized by applying anesthetic eye drops. You will be made to sit in front of the LASER machine and your eye specialist will place a small lens on your eye and direct the LASER light in to the eye. You will notice bright light flashes and most often no pain.
Alternately your doctor may deliver the LASER after making you sleep on a couch; in this technique no lens will be placed on your eye.
You will be requested to move your eye in different directions to enable the doctor to treat all the areas of the retina.
You can go home after the procedure and carry on with your normal activities. However, reading and performing near work may be difficult for a few hours because the pupils are dilated. There are no special dietary restrictions after LASER. You can wash your hair or face.
Rarely, if you are particularly light sensitive, your doctor may suggest an anesthetic injection so that you are more comfortable during the treatment.
You may be advised to sleep with head elevated and not to bend or lift heavy weights these are not precautions after LASER. These suggestions help prevent bleeding from the abnormal blood vessels.
Does LASER treatment restore vision?
LASER therapy for macular edema, mainly prevents additional vision loss but may also improve vision to some extent.
LASER for new blood vessel growth helps prevent complications such as bleeding inside the eye and retinal detachment.
LASER therapy will not make the blood go away it only decreases chances of further bleeding
Diabetes cannot be cured only controlled. Diabetic retinopathy may progress even after LASER or
What are the complications of laser treatment?
During the procedure, some people may find the light too bright, resulting in watering. Temporary vision loss lasting for a few minutes usually occurs immediately after the treatment. Blurred vision and inability to read may last until the effect of dilating medicines wane.
An assiduous person may notice decreased side-vision and also that it takes longer to see things when he or she enters a dark room. These side-effects cannot be prevented and are a small price to pay for avoiding blindness due to diabetic retinopathy.
What is Vitreous Surgery?
Vitreous surgery is microsurgery of the eye using 3 <1mm incisions. This surgery is used to treat complications of diabetic retinopathy such removal of bleeding inside the eye and repair of retinal detachment. Most patients get better with a single surgery while a few may need more than one surgery for visual improvement.
What is Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)?
As in other organs, the retina is also not completely developed in a premature baby. In a few premature babies, retinal blood vessels may develop abnormally causing bleeding and retinal detachment in the eye. This is called Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP). Without prompt treatment, the baby may become blind or have poor vision for life.
Do all babies need a retinal examination for ROP?
While it is essential that babies born with a birth weight less than 1700 gm or earlier than 35 weeks of pregnancy are examined for ROP, it is better that all premature babies born before 37-38 weeks irrespective of weight are checked for ROP. This is particularly important if the baby has had other problems such as lack of oxygen, infection, blood transfusion or breathing trouble, etc after birth.
When should the baby be examined for ROP?
The retinal examination should be completed before “day-30” of the life of a premature baby. In babies with very low birth weight (<1200 gm birth weight), the examination should preferably be done earlier (at 2-3 weeks of birth).
What if baby has been diagnosed as having ROP?
Most often ROP does not need treatment, but you may have to visit the retinal specialist at periodic intervals to ensure that the retinal growth is satisfactory and ROP is regressing.
In few babies, ROP may progress and may need treatment. Treatment is most often with LASER delivered much the same way as the eye is examined. Each treatment session will take around half hour and the child is not subjected to general anesthesia. Rarely a freezing treatment (cryopexy) may be necessary. The treatment helps stop further growth of abnormal vessels and prevent vision loss.
If treatment is required, prompt treatment is essential.
Will baby have normal vision after LASER treatment
Most babies have reasonably good to normal vision, depending on the severity of the disease.
Will baby need surgery?
Rarely, ROP progresses despite the LASER or if LASER is not performed in time. In such children complicated surgery may be necessary to retain some vision or to give some vision. Children who need surgery usually have advanced disease and may not enjoy normal vision. Surgery for advanced ROP also has a higher chance of failure.
What is epiretinal membrane in the retina and what are its symptoms?
Membranes that form over the surface of the retina are called epiretinal membranes. They usually occur in patients over 50 years of age. The membrane when it lies over the central retina (macula), it can block the light; the membrane can also contract and distort the retina. This distortion will be of the retina causes visual disturbances what one sees will appear distorted or slanted. Double vision can also occur; things can appear small or large when compared with the other eye. The condition may progress slowly and a small number of patients may have poor vision.
What to expect after macular hole surgery? What are the complication rates?
You may have to maintain face down head positioning for 16-18 hours a day for a couple of weeks so that the gas we inject in to the eye is able to do its bit for closing the hole. If you have been having the hole for 2 years or lesser, there is 70-80% chance of hole closure after surgery. Vision may not be normal after surgery but improvement much as three lines of letters seen on the visual acuity testing chart can be expected.
What is CSCR?
In central serous chorio-retinopathy(CSCR), some fluid collects under the central retina (macula). Because of the fluid, you will see a relatively black patch wherever you wish to see and also distortion of images. Straight lines will appear bent and objects may appear smaller or larger than they are. Some vision loss also occurs.
What are the risk factors for developing this disease?
CSCR is typically a disease of young, adult males. Men, aged between 25 and 45 years represent about 85-90% of the patients. An anxious, emotionally stressed personality (Type A), use of steroids for various ailments (arthritis, asthma, skin allergies or organ transplant), pregnancy are risk factors for CSCR to occur.
What is the natural course of this disease?
Most often CSCR heals by itself in 3-4 months with normal to near normal vision. If the CSCR does not heal by this time period, treatment may be necessary. In people needing early restoration of vision for professional or personal needs, CSCR can be treated earlier.
What is the treatment of CSCR?
There is no medical treatment for CSCR. Before treatment, a FFA test should be done to identify the leaking point. An OCT test may also be necessary. Following these tests, laser treatment is done to seal the leak. It may take a 4-6 weeks for improvement in vision to occur.
Does this disease recur?
CSCR may recur in half to one-third of patients and 10% patients may have 3 or more recurrences. In most cases, the recurrences occur within a period of one year.
What is AMD?
Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is a disease affecting the central sensitive part of the retina, called as themacula. The risk of acquiring this disease increases with advancing age. It has become a major cause of visual disability in older populations all over the world.
What are the types of AMD?
AMD can present either as a dry or wet form. Dry AMD is characterized by the presence of yellow deposits (accumulated debris from the aging retina), called drusen. With the passage of time these deposits enlarge and merge; the retina becomes atrophic (geographic atrophy) causing loss of vision.
What are the symptoms of AMD?
Dry AMD causes a gradual loss in central vision and in advanced cases, severe vision loss may also occur.
Patients with wet AMD may develop severe visual loss more often. In early stages of wet AMD, distortion and waviness of lines may be the early symptom. Reading small print will be difficult and one may notice that letters or words in a sentence go missing. Once bleeding occurs this is seen by the patient as a dark spot, which constantly obstructs central vision. Without treatment central vision may continue to worsen over time and patients may need assistance to carry out their daily routine activities.
How is AMD detected?
The best way of detecting AMD is getting a regular retinal examination done, especially, after the age of 50. An Amsler’s test (a graph-paper like sheet) is very useful for detecting early changes in central vision. It can be done at home, by people having dry AMD, and at risk of developing wet AMD.
The retinal specialist will perform a complete eye examination and may order tests such as FFA, ICG angiograms andOCT. These tests will help select the ideal treatment for each patient.
What are the risk factors for AMD?
As the name suggests, the main risk factor is advancing age. The other risk factors are
Smoking
Hypertension
Obesity
Race (whites more than African Americans)
Gender (females more than males)
What are the treatment options for dry AMD?
No treatment is useful in advanced dry AMD (geographic atrophy). Treatment does have a role in reducing the risk of progression of the intermediate stages to the advanced stages (of dry or wet AMD). The Age Related Eye Diseases Study (AREDS) has recommended 500 milligrams of vitamin C, 400 International Units of vitamin E, 15 milligrams of beta-carotene (equivalent to 25,000 International Units of vitamin A), 80 milligrams of zinc as zinc oxide, and 2 milligrams of copper as cupric oxide as dietary supplement in AMD. This formulation that is available in capsule form is neither a cure for AMD nor will it restore lost vision. It only delays the onset of advanced AMD.
What are the treatment options for wet AMD?
The treatment of wet AMD has evolved in the last 5-6 years from limiting degree of vision loss to maintaining and improving existing vision. Anti-VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) therapy and Photodynamic Therapy (PDT), or a combination of the two, form the basis of modern day treatment of wet AMD.
Before treatment, FFA test and OCT and in some patients ICG angiogram will be performed. This will help the eye specialist decide on the area of treatment, best treatment option and help in assessing the response to treatment.
Anti-VEGF therapy Anti-VEGF therapy works by blocking the action of VEGF, the molecule that promotes the growth of the abnormal blood vessel under the retina (CNVM). These drugs are injected directly inside the eye, to provide maximum concentration where it is needed that is near the CNVM.
Pegaptanib (Macugen) and Ranibizumab (Lucentis) are drugs that are FDA (US drug regulatory authority) approved for treatment. However another molecule, Bevacizumab that is essentially a drug approved for use in colorectal cancer patients is being used widely across the world by ophthalmologists to treat wet AMD. This is also an anti-VEGF agent with a cost advantage over the FDA approved drugs.
Bevacizumab is however not approved by the FDA for eye use National Eye Institute, a premier eye research organization in USA is funding a study evaluating the use of Bevacizumab in wet AMD patients. The results of this study, if favoring Bevacizumab, may give official recognition to this drug. Until then Bevacizumab use will remain “Off-Label”.
What are the side-effects of these injections?
Some discomfort, rarely pain, redness of the eye may be present on the day of the injection and a day or two later.
These injections have to be repeated at monthly or 6 weekly intervals for a year or two and this means that the patient has to make repeated visits to the clinic and also undergo regular consultations and investigations.Combining these injections with other treatment such as Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) may however decrease the need for re-treatments and seem to be favored by most retinal specialists.
These injections are injected in to the eye this may very rarely be associated with a serious infection of the eye called endophthalmitis. If such a complication were to occur, the patient will need injection of antibiotics in to the eye or a surgery (vitrectomy) for controlling the infection. This will adversely affect the vision. This complication is however rare and may affect 1-2 out of 1000 patients.
These medicines are new developments and long-term side effects are not known at the moment. There is a possibility that these medicines may have some systemic side effects like increasing risk of stroke in people who are predisposed.
Is the injection painful?
The injections are given after applying anesthetic eye drops or anesthetic injection there may be slight discomfort and soreness on the day of injection, but not pain. To decrease the risk of serious infection after injection, you may have to use antibiotic eye drops for 2-3 days prior to and after the injection and the procedure will be performed under sterile precautions (like preparing for an operation). You will have to continue using the antibiotic eye drops after the injection and avoid washing your hair for 3 days. You need to avoid water entering the eye for 3 days as well. The symptoms you need to be wary of are
Decreased vision
Pain
Increasing redness
Discharge from the eye
Swelling of the lids
If you notice any of these symptoms you need to consult your doctor immediately.
Corneal & Trauma Center
What is Cornea?
Cornea is like a transparent watch glass situated in front of the eye. It appears black or brown from outside due to the dark structures situated underneath.
Who requires Corneal Graft?
Cornea can become cloudy or opaque leading to decreased vision or even severe loss of vision. The opacity of cornea is caused due to any severe infection (corneal ulcer) or trauma / injury. These patients will require Corneal Grafting Surgery.
What is Corneal Graft?
Corneal Grafting or KERATOPLASTY is carried out to replace the damaged cornea with a clear one with sutures. This clear cornea is obtained from the donated eye of a deceased person. The latest techniques involve sutureless corneal transplant techniques like DALK- Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty and DSEK- Desemets Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty.
What is myopia?
Myopia or short-sightedness is a condition in which the rays of light reaching the cornea (the clear front portion of the eye) are focused in front of the retina (the light sensitive portion of the eye). The resulting vision is thus, not clear and close objects are seen well than those at a distance.
How is Myopia Corrected?
Corrective Lenses: Contact lens and spectacles alter the path of the light rays to achieve precise retinal focus.
Corneal Graft Operations
Cornea is like a transparent watch glass situated in front of the eye. It appears black or brown from outside due to the dark structures situated underneath.
Keratectomy (myopia)
Myopia or short-sightedness is a condition in which the rays of light reaching the cornea (the clear front portion of the eye) are focused in front of the retina (the light sensitive portion of the eye). The resulting vision is thus, not clear and close objects are seen well than those at a distance.
C3 Linking (Corneal Collagen Cross Linking)
Keratoconus is a progressive disease of the cornea in which the corneal tissue is weak. This results in gradual thinning and bulging outward of the cornea. As the name Keratoconus implies Kerato – meaning cornea, Conus – meaning cone, the condition results in conical protrusion of the cornea.
The patients may present with complaints of blurry and distorted vision. This results due to the abnormal curvature of the cornea leading to irregular astigmatism. The chances of suffering from this problem is one in two thousand. Approximately half of the keratoconus patients need help beyond corrective glasses. The other modalities of treatment available now such as Rigid Gas Permeable lenses, Intact are often uncomfortable to the patient and restricts the life style.
In advanced Keratoconus the only option to restore vision is a corneal transplant. This new modality of treatment known as a collagen cross-linking with Riboflavin has proven to strengthen the weak corneal structure. During this 30 minute cross linking treatment custom made Riboflavin eye drops are applied to the cornea which is then activated by UV-A light. Under the influence of the UVA, chemical bonds form in the corneal collagen lamellae, which are the structural backbone of the corneal tissue, and this strengthens the cornea and stiffens the tissue. The increase in tissue rigidity appears to slow or stop the progression of the corneal thinning and shape changes that normally occur in keratoconus.
Keratoconus is a debilitating condition that affects vision in people starting their careers and is hence a serious problem. However, with recent advances in instrumentation, early diagnosis is possible, and with newer modalities of treatment available in the form of cross linking to patients who had no hope science has made yet another mark in helping people with a progressive blinding disorder.
Glaucoma Assesment & Treatment
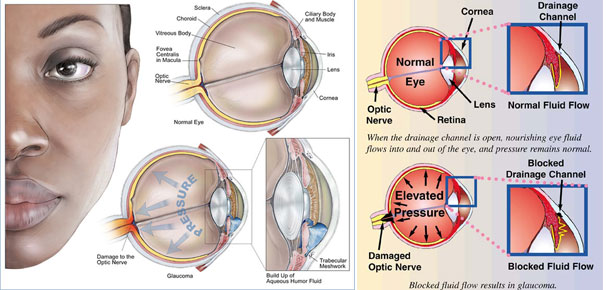
What is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is a very dangerous eye disease and a silent killer of vision too and second most common cause of blindness in the world. As it does not display any early warning signs, many sufferers do not know that they may have Glaucoma, and by the time there is a noticeable symptom, an irreversible could have already occurred.
How is Glaucoma detected?
Since Glaucoma has no noticeable symptoms. It can only be diagnosed through a routine Eye check up by measuring the Eye Pressure and some specific tests of which the Gold Standard test is Field of vision Test (Perimetry). Only an Eye Examination can detect glaucoma.
Who are at risk for Glaucoma?
Those over 40, years of age having a family history of Glaucoma, high Myopia, high blood pressure or diabetes and those who have suffered any eye injuries in the past or have used steroids are all at high risk of Glaucoma. While older adults are at high risk, it can strike at any age.
Can I have Glaucoma even if I have Normal Vision?
Yes. Glaucoma often goes unrecognized until significant permanent damage and some loss of sight has occurred which is peripheral, it is only field of vision- through Perimetry testing it is diagnosed.
How is Glaucoma Treated?
Glaucoma is usually controlled with eye drops taken daily. These medications lower eye pressure, either by decreasing the amount of aqueous fluid produced within the eye or by improving the flow through the drainage angle.
Never change or stop taking your medications without consulting your ophthalmologist.Once you are taking medications for Glaucoma, your ophthalmologist will want to see you more frequently. Typically you can expect to visit your ophthalmologist every three to four months. This will vary depending on your treatment needs.
If medications don’t work and symptoms become severe then a Surgery is recommended.
Are you over 40 years? YES/NO
Does anyone in your family have Glaucoma? YES/NO
Do you have high myopia? YES/NO
Do you have High Blood pressure or Diabetes? YES/NO
Have you used Steroids for long time? YES/NO
Do you have eye injuries in the past? YES/NO
If answer is “YES” to any of above questions, you are at risk for Glaucoma.
It is an eye disease that can cause loss of vision. Often called as “Sneak Thief Of Sight” , Glaucoma is deadly because there are no early warning signs. In fact, you may be suffering from Glaucoma but do not know it. By the time you experience some vision loss, an irreversible damage has already occurred. Fortunately treatment can save your eyes if Glaucoma is detected early.
Squint evaluation & Treatment
Oculoplasty Procedure
The structures around the eye namely the eye socket (orbit) with its components of muscles, fats, nerves and bone, the tear duct system composed of tear secreting and tear draining structures and finally the eyebrows and eyelids provide a very important function of protecting the eye within. Infections, injury and tumours may affect the above structures and not only affect vision but may even cost patient’s life. Oculoplasty deals with such conditions in addition to providing surgical enhancement of the ageing face- the aesthetic surgery.
Defects of the eyelids arise as birth defects, from injuries either at school, home or at work and not infrequently from benign and malignant tumours of the eyelid . By use of refined techniques of eye plastic surgery, such eyelids can be restored to normal structure and function. Often times eyelids can be droopy causing increasing strain or even lazy eyes in children.In such situation ‘Ptosis surgery’ restores to a more acceptable form and function and thereby help treat this form of childhood blindness.
Watering of the eyes is a common complaint in the young and the old. While it can be related to dry eyes, more commonly a blockage of the drainage system may also result in swelling, discharge and even acute infections. Depending upon the cause, various lacrimal system drainage surgeries may alleviate the symptoms and lifelong misery.
Problems of the eye socket (orbit) include fractures, inflammations and even tumours. Depending upon the presentation, appropriate investigations helps in tailoring treatment to the patient which helps rehabilitate not only the sockets but the patient as a whole.
Loss of an eye may result from severe infections, injury or cancer. Left with a permanent disfigurement with physical and psychological consequences, various interventions tailored to the individual patient like prosthesis fitting with or without socket surgery more or less restores normal appearance to aid the patients lead socially acceptable normal lives.
Thyroid eye disease is a common condition where eye disease may be related to general health. This debilitating disease not only results in abnormal facial appearance but also may lead to blindness. While most of them can be managed with medications alone, restorative and rehabilitative surgery may help in preventing/reversing blindness and disfiguration.
Paediatric Ophthalmology
How do the eyes work together?
With normal vision, both eyes focus at the same spot. The brain then fuses the two pictures into a single three-dimensional image. This three-dimensional image gives us depth perception. When one eye turns, two different pictures are sent to the brain. In a young child, the brain learns to ignore the image of the misaligned eye and sees only the image from the straight or better eye. The child then loses depth perception and the unused eye becomes a lazy eye.
Adults who develop strabismus often have double vision because the brain is already trained to receive images from both eyes and cannot ignore the image from the turned eye.
Causes of Strabismus
The exact cause of strabismus is not fully understood. Six eye muscles, controlling eye movement, are attached to the outside of each eye. In each eye, two muscles move the eye right or left. The other four muscles move it up or down and at an angle.
To line up and focus both eyes on a single target, all of the muscles in each eye must be balanced and working together, the muscles in both eyes must be coordinated. The brain controls the eye muscles. A cataract or eye injury that affects vision can also cause strabismus.
Strabismus
Strabismus is a condition in which the eyes are misaligned and viewing at different directions. One eye may look straight ahead, while the other eye turns inward, outward, upward or downward. You may always notice the misalignment, or it may come and go. The turned eye may straighten at times and the straight eye may turn.
Strabismus is a common condition among children. It occurs equally in males and females. Strabismus may run in families. However, many people with strabismus have no relatives with the problem.
It is a myth and belief that strabismus is lucky, but it has to be corrected at a very early age to prevent vision-loss in future.
Diagnosis of Strabismus
The main symptoms of strabismus are an eye that is not straight. Sometimes children will squint one eye in bright sunlight or tilt their head to use their eyes together.
Strabismus can be diagnosed during an eye examination. It is recommended that all children have their vision checked by their pediatrician, family doctor or ophthalmologist (eye specialist) at or before their fourth birthday. If there is a family history of strabismus or amblyopia, an ophthalmologist can check vision even earlier than age three.
Amblyopia / Lazy Eye
Good vision develops during childhood when both eyes have normal alignment. Strabismus may cause reduced vision, or amblyopia, in the weaker eye. The brain will recognize the image of the better-seeing eye and ignore the image of the weaker or amblyopic eye. This occurs in approximately half the children who have strabismus. Amblyopia can be treated by patching the “good” eye to strengthen and improve vision in the weaker eye. If amblyopia is detected in the first few years of life, treatment is usually successful. If treatment is delayed until later, i.e. > 12 years, amblyopia usually becomes permanent. As a rule, the earlier amblyopia is treated, the better the visual result.
How is strabismus treated?
- Preserve vision
- Straighten the eyes
- Restore binocular (two-eyed) vision.
After a complete eye examination, an ophthalmologist can recommend appropriate treatment.
In some cases, eyeglasses can be prescribed for your child. Other treatments may involve surgery to correct the unbalanced eye muscles. Covering or patching the strong eye to improve amblyopia is often necessary.
Paediatric Cataract
Orthoptics – Speciality Orthoptic Department with State – of – the – art computerised ORTHOPTIC Diagnosis and Therapy.
Optometry and Contact lens Clinic
What are contact lenses?
Contact lenses are small visual devices made with curved pieces of plastic shaped in a way to conform directly to the wearer’s eye. They provide an artificial refracting surface to the human eye and are used to correct vision problems like myopia and hypermetropia. Contact lenses aid in eye focusing in the same manner as spectacles do. Apart from these corrective measures, contact lenses can also be used for cosmetic and therapeutic reasons.
Advantages of Contact Lenses
Contact lenses are capable of correcting most of the problems that spectacles can as well as some additional ones that glasses cannot.
People not satisfied with their appearance using glasses can opt to use contact lenses for improved appearance. Contact lenses are not in the danger of slipping off, getting wet, or fogging up, which can easily happen with spectacles.
Extremely hypermetropiac people or those who have had cataracts removed, feel better wearing contact lenses as compared to spectacles, which in these cases produce uneven vision. Moreover, contact lenses give improved vision for people with damaged corneas due to disease or injury. Also for sportsmen, wearing contact lenses prove to be more practical as in the case of those where wearing spectacles pose a problem in their jobs. In addition to all these, contact lenses provide better side vision compared to glasses.
Uses of Contact Lens
The primary use of contact lenses is to correct myopia (short sightedness). They can also be used to rectify hyperopia, astigmatism, presbyopia and aphakia. Rigid lenses are used to correct irregular corneal trauma. Soft lenses are used as bandages for conditions like bullous keratopathy, recurring corneal erosion as well as to increase comfort, vision and postoperative wound healing.
How to wear Contact Lens–
- Put the contact lens on your index finger.
Note: Check to see that your contact lenses are on its proper side. If the edges are protruding outward, then it’s on the wrong side. - Using your middle finger of your other hand, you can pull the lower eyelid down You can then use your middle finger of the opposite hand to pull your eyelid up.
- Place the contact lens in your eye, make sure not to blink.
Note: put the bottom of the contact lens before the top part. Use your finger to make sure that the contact lens is fully in. - Move the contact lens towards your eye calmly and steadily.
Note: After placing the contact lens on your eye, gently move it so it is centered over your iris (circular, colored part of eye). - Blink your eye to adjust the lens.
TYPES OF LENSES AVAILABLE AT AMDAVAD EYE LASER HOSPITAL
Daily Disposable Contact Lenses
Daily disposable lenses are the most popular contact lens for many reasons. They are convenient and easy to use because you don’t have to hassle with cleaning. They are also healthier for those with allergies because they are hygienically clean every morning. Please consult your eyecare specialist for advice.
These contacts can be worn for up to one month, as directed by your optometrist. This means that at the end of every day you remove your lenses and clean them before reinserting them.
This is because your tears contain mineral deposits which can build up on your lenses. If you do not clean them properly then these deposits can cause discomfort and even infection.
Toric Contact Lenses
Toric Lenses are designed for those with astigmatism. A toric contact lens has two different powers or curvatures so that it can correct for both astigmatism and either myopia (near-sightedness) or hyperopia (far-sightedness). Increasingly, toric contact lenses, which typically combine the effects of a cylindrical lens with that of a spherical lens, are being prescribed for people who are astigmatic and also need help with their far-away or close-up vision.
Computer Vision Syndrome
Computer Vision Syndrome
The prevalence of eye symptoms among computer users ranges from 25-93% as reported by various investigators. Computers have become indispensable in the workplace. The professionals spend increasing amounts of time sitting at their computer work-stations. At the same time productivity is increasing and workers are exposed to working at high speed and to tight deadlines.
The combination of fixed and constrained body postures, work overload and unsuitable workstations can lead to health problems. The most common complaints among computer users are aches and pains in the shoulder, forearm, wrist, hand, back and neck and eye strain.
Clearly a large percentage of computer workers experience eye symptoms and subsequently seek eye care. Computer vision syndrome is that set of eye care. Computer vision syndrome related to near work which are experienced during or related to computer use. These symptoms can include:
- Head aches
- Eyestrain
- Blurred vision
- Dry or irritated eyes
- Neck aches
- Back aches
- Light Sensitivity
- Double vision
These symptoms are often a result of a combination of three factors:
- Your workplace conditions
- Your working habits
- Tour visual condition
Discomfort Factors
- Nature of the task
- Length of time spend at the computer
- Reduced rate blinking
- Lack of coordination between the design of the workstation and the design of the glasses or contact lenses used for the task.
Here are some examples of situations that usually increase user discomfort especially to the eyes.
- Intense tasks such as games.
- Tasks with few breaks from the screen.
- Tasks which require constant looking from the copy to screen such as data entry.
- Detailed tasks such as desk top publishing or Computer Assisted Design (CAD).
- Eye level placement of screens causes eyes to be wide open causing faster drying.
- Eye level screens are too high for most bifocal wearers unless they have specially designed glasses for this task.
- Many glasses exacerbate the restriction of movement which is a consequence of most computer tasks causing neck, shoulder, and arm problems.
The average rate of blinking is 12 to 15 times per minute. This is frequently reduced during intensive tasks, leading to visual fatigue and dry eyes. Therefore, reading from a screen reduces blinking, which in turn, leads to discomfort.
Lighting
Good lighting design can significantly help reduce discomfort due to glare. Light leaving the fixture can be directed so that it goes straight down and not into the eyes of the room occupants. This is most commonly accomplished with the louvers in the luminaries or fixture. An even better solution is indirect lighting in which the light is bounced off the ceiling – resulting in a large low luminance source of light for the room.
When you sit, the weight on your lower back is one and a half to two times bigger than when you stand. A good chair must accommodate your body sizes and must be adjustable in the following areas:
Height of the seat
When your feet rest comfortably on the floor, a 90 degree angle between upper and lower legs is desirable. In this position, your upper legs are virtually horizontal.
Depth of the seat
The clearance between the front edge of the seat and the back of your knee must fit a clenched first.
Backrest
The backrest must support the area from the upper ridge of the pelvis to the shoulder blades. The curve in the backrest must support the hollow in your lower back. An adjustable tilt is desirable.
Perimetry
We at “Amdavad Eye laser Hospital” always worked towards providing the best possible eye-care facilities to our patients. In that direction we are happy to inform you that a new high precision equipment having most advanced features for the early detection and treatment of Glaucoma has been recently acquired by us.
You may be aware of the fact that Glaucoma is a very dangerous eye disease and a silent killer too, because it does not display any early warning signs. Many sufferers do not know that they may have Glaucoma, and by the time there is a noticeable symptom, an irreversible damage could have already occurred.
Those over 40 years of age having a family history of Glaucoma, high Myopia, high blood pressure or diabetes and those who have suffered any eye injuries in the past or have used steroids are all at risk of Glaucoma.
Fortunately, with the advancement of technology, it is now possible to detect Glaucoma in its very early stages and save your vision. In order to provide a fool-proof, extremely precise & accurate early detection facility, we have acquired OCTOPUS 900 Automated Perimetry with Eye Suite software and dual reporting, the latest in technology from Switzerland. It is the first machine of its kind in Gujarat.
We hope that this information will be useful to you. If you have any queries or need more details, please contact Eye Care Hospital. Our doctors & staff will be happy to respond to you quickly.
In future, we will keep you informed from time to time about our activities towards technology up-gradation in our facilities to serve you better.
Diabetic Eye Clinic
What happens to the retina in diabetes?
The pathological change in diabetes leads to the lack of blood supply or ischemia of the retina and hypoxia of retinal tissues. Long standing hypoxia leads to new vessels formation. These new vessels are fragile and bleed very easily. Excessive bleeding in the eye leaks to vitreous haemorrhage and loss of vision.
In some areas there is the swelling of the vessel wall and leakage of the fluid leading to retinal edema. Involvement of macula, the central portion of the retina leads to severe drop on vision. Scar tissue can also grow from ruptured blood vessels which will contract and pull the retina, detaching it with resultant loss of vision.
- Major causes of irreversible blindness in old age.
- Longer the duration of diabetes greater is the severity of retinopathy.
- Hypertension, Renal disease, Hyperlipidemia, Obesity, Smoking, Anemia has an adverse on Diabetic Retinopathy.
Diabetic Eye Clinic:-
Diabetes is the single most important cause for death and disability world wide. It affects almost all organs in the body. It is estimated tat presently 19.4 million individuals are affected by this deadly disease and it is likely to go upto 57.2 million by 2025. With this statistics, every 5th diabetic in the world will be an Indian by 2025.
Diabetic retinopathy is essentially a disease process, which affects the blood vessels of the retina. It is also an indicator of the status of the blood vessels elsewhere in the body e.g. Kidney, heart, etc.
Precautions to be taken
- Good control of diabetes by medication, diet and exercise
- Control of associated disorders like hypertension, renal disease, hyper lipidemic status is a must
Diabetic retinopathy patients with hypertension, renal disease or pregnancy should have regular ophthalmic checkup every 6 months - Diabetic retinopathy patients who have undergone Laser should have regular ophthalmic checkup every 3 months
- All diabetics should have a mandatory eye checkup once in a year
At Amdavad eye laser Hospital, we have a fully equipped diabetic retinopathy clinic. red free photographs and angiography purposes to diagnose various vascular disorders including Diabetic Retinopathy.Ophthalas 532 eye lite (Green laser by Alcon) is used for Focal, Grid and pan retinal photocoagulation in different stages of Diabetic Retinopathy.
For advanced diabetic retinopathy, which requires surgery, we have Carl Zeiss Operating Microscope which is the world’s best microscope from Germany, also used for all complex Vitreoretinal surgeries. Amdavad eye laser Hospital is the one of the few centers in India to use the BIOM (Binocular Indirect Ophthalmic Microscope) to visualize the retina during surgery.New Millennium Vitrectomy 2000 (Oscar Vision Tech) Vitrectomy Machine is used for sophisticated surgeries like removing blood from inside the eye, removing foreign body from the eye, and for complicated retinal detachments.The institute is also equipped with Endo Illuminator, Endo laser and Micro Vitreous instrumentation for advanced vireo retinal surgeries.
Botox / Aesthetic Eye Clinic
Botulinum toxin has come a long way from once being considered as a dreaded toxin to the present day when it is being most sought after for its cosmetic application.
Three preparations of botulinum toxin are commercially available at present.
- 1. Botox (Allergan Inc., Irvine, CA, USA)
- 2. Dysport (Ipsen Pharmaceuticals, France) are the type A toxins.
- 3. Myobloc (Elan Pharmaceuticals, San Diego, CA, USA) is the type B toxin.
Aesthetic oculoplasty
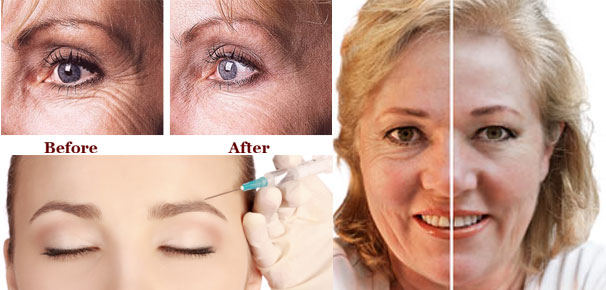
The use of botulinum toxin for decreasing the dynamic wrinkles in the facial region has become the most popular indication for its use now ever since Carruthers et al. reported its use for dynamic wrinkles in the glabellar area in 1992.
Glabellar frown lines
The glabellar wrinkles are caused by the actions of corrugator supercilli, depressor supercilli and procerus muscles(. 2.5-5 U of botulinum toxin type A are injected at five to seven sites into both corrugators and into the procerus muscle which provides relief for upto 6 months.
Horizontal forehead wrinkles
These occur due to the chronic action of the underlying frontalis muscles. Injection of botulinum toxin type A (Botox) in four to eight sites spaced evenly over the forehead may relax the muscle and soften these lines. The injections are typically given 2-3 cm above the orbital rim using 2.5-5 U per injection sites.
Periocular crow’s feet
The contraction of the lateral orbicularis fibers, zygomaticus and risorius muscles gives rise to dynamic wrinkles spreading out from the lateral canthus, known as the crow’s feet). Three to four injections of 2.5-5 U of Botox into lateral orbicularis oculi are required for effective treatment of crow’s feet.
Chemical brow lift
Botulinum toxin can be used to create a chemical browlift by selectively paralyzing the depressors of the eyebrow.
Other aesthetic facial applications of botulinum toxin include ‘bunny lines’, peri-oral treatment, dimpled chin, ‘marionette lines’ and platysmal bands.
Presbyopia (BETALA)
What is Cornea?
Cornea is like a transparent watch glass situated in front of the eye. It appears black or brown from outside due to the dark structures situated underneath
Who requires Corneal Graft?
Cornea can become cloudy or opaque leading to decreased vision or even severe loss of vision. The opacity of cornea is caused due to any severe infection (corneal ulcer) or trauma / injury. These patients will require Corneal Grafting Surgery.
What is Corneal Graft?
Corneal Grafting or KERATOPLASTY is carried out to replace the damaged cornea with a clear one with sutures. This clear cornea is obtained from the donated eye of a deceased person. The latest techniques involve sutureless corneal transplant techniques like DALK- Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty and DSEK- Desemets Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty.
What is myopia?
Myopia or short-sightedness is a condition in which the rays of light reaching the cornea (the clear front portion of the eye) are focused in front of the retina (the light sensitive portion of the eye). The resulting vision is thus, not clear and close objects are seen well than those at a distance.
How is Myopia Corrected?
Corrective Lenses: Contact lens and spectacles alter the path of the light rays to achieve precise retinal focus.
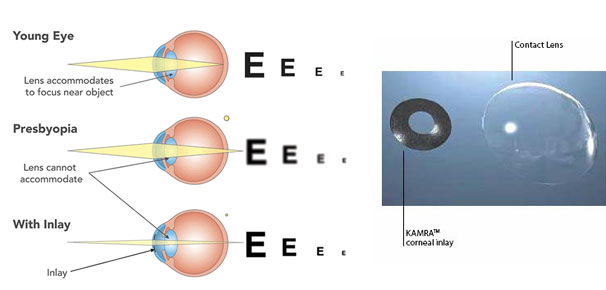
Conductive Keratoplasty
Conductive keratoplasty (CK) is a non-laser refractive eye surgery design ed to correct mild hyperopia and help people who are middle-aged and older reduce their need for reading glasses after they become presbyopic.
Refractec Inc. (Irvine, Calif.) markets the CK procedure under the trade name NearVision CK.
More About Conductive Keratoplasty
Unlike LASIK, PRK and other laser-based procedures, Near Vision CK uses low energy radio waves to reshape the cornea and restore near vision.
During the CK procedure, your eye surgeon uses a hand-held instrument with a tiny probe (smaller than a human hair) to apply low-level, radio frequency (RF) energy to specific spots that form a circular pattern on the outer part of the cornea.
Connective tissue then shrinks where the RF energy was applied, causing the circular band to act like a belt that “tightens” and steepens the cornea. This change in the curvature of the eye’s surface affects the way light rays enter the eye to bring near vision back into focus.
Unlike LASIK or PRK, no tissue is removed from the eye during a Near Vision CK procedure that takes only a few minutes.
CK also is being investigated as a way to correct certain types of astigmatism that create an irregular eye surface due to trauma or surgical incisions.
In conductive keratoplasty, low heat energy from radio frequency is applied through a probe to reshape your eye’s surface.
Conductive Keratoplasty and Monovision
If you have clear distance vision and your only problem is poor near vision due to presbyopia, conductive keratoplasty is performed on only one eye. This creates a mild form of monovision, meaning that one eye is corrected for near vision while the other eye is stronger for distance vision.
As may happen with monovision with contact lenses or a LASIK eye surgery procedure, your driving vision with this type of vision correction may be less sharp than it is when both eyes see clearly in the distance. So you may find a pair of eyeglasses for night driving useful after CK.
While CK can improve near vision, the procedure doesn’t cause as much blurring of distance vision as mono vision with contact lenses or laser vision correction procedures such as LASIK. Studies indicate that the CK procedure may alter the cornea in such a way that a slight multifocal effect is achieved, creating “zones” through which the eye may be able to see at different distances.
Prior to a conductive keratoplasty procedure, your eye doctor may recommend that you first wear a contact lens for near vision correction on one eye for a period of time to make sure you are able to adapt to monovision. But this is not a requirement. People who adapt well to a monovision contact lens fitting typically are able to tolerate a CK procedure.
During your CK consultation, your eye doctor may conduct another test that involves holding a +1.00 diopter lens for near vision correction in front of your non-dominant eye.
This way, you can experience (with both eyes open) what it is like to have one eye see better at a distance and the other eye see better close up.
If you notice a significant blurring of your distance vision during this test with both eyes open, you may not be a good candidate for the procedure.
If you still can see clearly across the room under these circumstances, you likely will adapt well to CK.
Are You a Good Candidate for CK?
You may be a good candidate for NearVision CK if your eyewear prescription has been stable for at least one year and you:
Are over age 40.
Have had good distance vision your entire life but now need reading glasses.
Are willing to accept slight distance blur
Is Vision Correction From Conductive Keratoplasty Permanent?
Even though CK effects are long-lasting, they are not permanent.
Also, effects of CK can be temporary because your eyes will continue to change as presbyopia worsens.
When you look at a reading glasses rack at the store, for example, you see +1.00 power readers for a 40-year-old, +2.00 power readers for a 50-year-old, +3.00 power readers for a 60-year-old and so on.
Even though you eventually will need reading glasses again after CK, you still may retain good intermediate vision, enabling you to see a computer screen and view a cell phone without glasses.
Great candidates for CK are those who want to delay the need for reading glasses.
And when reading glasses are needed, these candidates still might appreciate having functional vision in the intermediate range.
Steps To Take Before Undergoing Conductive Keratoplasty
If you are considering NearVision CK, you first need to choose a refractive surgeon who is experienced with the procedure. Your doctor will examine your eyes thoroughly to determine if you are a good candidate.
During your consultation, an instrument called a corneal topographer will be used to create a detailed map of the curvature of your cornea. The topographer doesn’t touch your eye, and the measurement is similar to having a close-up photograph taken of your eye’s surface.
The corneal topography map will display the various steep and flat corneal curvatures that the surgeon must take into consideration while conducting the procedure.
What Happens During CK?
Conductive keratoplasty can be performed in the ophthalmologist’s office. The surgeon will apply some anesthetic eye
drops to your eyes and then use a small support device called a speculum to keep your eyelids open and prevent blinking.
Using a rinse-away dye, the surgeon will imprint a treatment pattern on your cornea, showing where the radio frequency energy should be applied.
A hand-held probe then is used to deliver the energy to a specific depth within the cornea at these spots. The entire procedure takes only a few minutes.
NearVision CK is painless, but some people say they feel a slight pressure on the eye.
If you are being treated for hyperopia, both eyes can be addressed during the same visit. In this case, the procedure involves virtually no down time.
Steps To Take After a Conductive Keratoplasty Procedure
After surgery, you will be given a prescription for eye drops that help prevent infection and reduce inflammation. Some surgeons may ask you to wear special bandage contact lenses for a few days, to minimize discomfort.
You can leave the doctor’s office right after conductive keratoplasty, although someone else must drive you home.
You may experience a foreign body sensation when the topical anesthetic wears off (about 20 to 30 minutes after the procedure), similar to the feeling of having a piece of dirt or debris in your eye. This sensation usually subsides within 24 hours.
Although you typically will be able to function normally the day after surgery, you may be slightly nearsighted for a few weeks or even months. This may cause noticeable blurring of your distance vision.
You also may experience mild vision fluctuation, and your eyes may be sensitive to bright light after surgery. If these side effects occur, they usually will clear up within a few weeks.
For at least one week after surgery, you should avoid swimming, using a hot tub or participating in any other activities where water may splash into your eyes. When showering during this period, keep your eyes closed as much as possible, and direct the spray away from your face.
When To Avoid CK
You should not undergo the NearVision CK procedure if you wear a pacemaker for regulating your heart beat. The radio frequency equipment may interfere with the proper operation of these electronic devices.Also, your eye doctor will advise you if you have any other conditions such as severe dry eyes that would eliminate you as a candidate for CK.
What To Expect After Conductive Keratoplasty
CK is one of the safest procedures performed for near vision correction because, unlike other procedures, it does not involve cutting or removing tissue. Instead, CK gently reshapes the cornea with radiofrequency waves to reduce the need for reading glasses.
Therefore, complications sometimes associated with other vision correction procedures, such as dry eyes, are less likely with CK, because it is relatively non-invasive.
Though the near vision benefits of CK will not last indefinitely, the procedure often is an excellent choice for people who want relief from reading glasses and have proper expectations about CK.
Even if reading glasses are needed again several years after CK, the procedure usually continues to provide improved vision without glasses for computer use and other visual tasks at arm’s length.
Kamra Inlay
Kamra Inlay in
If you are over the age of 40, you’ve probably noticed that near objects are beginning to appear out of focus. You may be experiencing a condition called presbyopia. With presbyopia, the natural lens of the eye has lost its flexibility. The lens does not readily change its focus from distance to near. As a result, near objects are blurry. Until recently, reading glasses were the primary option for people with presbyopia. However, many people prefer not to wear reading glasses because they can be inconvenient to use, inaccessible when needed the most, or unappealing for cosmetic reasons.
One of the options to decrease dependency on reading glasses is the Kamra inlay.
Other surgical options include monovision LASIK or PRK in which one eye is treated for distance vision and the other for near,
monovision refractive lens exchange, or a refractive lens exchange with a multifocal intraocular lens. At Our place a comprehensive evaluation including
digital testing is performed to determine the best choice to provide both distance and reading vision.
What is the kamra inlay?
The Kamra inlay is actually a very simple device and utilizes an optical principal that has been known for thousands of years but that has only relatively recently been adapted for use in the eye-care field.
The Kamra inlay is a microscopic black ring with a tiny aperture or hole in the centre. It’s smaller than a contact lens, lighter than a grain of salt, and virtually invisible when inserted. The small aperture increases the depth of focus to enhance near objects and maintains distance vision. The inlay is inserted beneath a LASIK flap or pocket to enhance reading vision. The procedure is reversible.
Kamra Inlay with a small central opening that helps focus vision for reading.
The Inlay is much smaller and thinner than a contact lens.
“The corneal inlay can be performed at the same time as the LASIK procedure or in patients that have previously had LASIK or PRK”.
The inlay has a diameter of 3.8 mm with a central opening of 1.6 mm and a thickness of 5 microns. This thickness is 1/10th the thickness of a human hair. There are 8,400 high precision, laser etched micro-openings in the opaque part of the disc. These holes help maintain a healthy cornea by allowing glucose, oxygen and other metabolites to pass through
“Patients that have had other types of eye surgery, whether it be laser vision correction or cataract surgery can now benefit by the Kamra inlay. The Kamra inlay is a revolutionary device that is so simple in principle but with a dramatic effect in its ability to restore reading vision”.
How is the Procedure Performed?
The Kamra inlay is implanted under a LASIK flap once the prescription has been lasered to -0.75. For patients who do not require simultaneous LASIK, the Kamra inlay is placed into an intra-corneal pocket created by the femtosecond laser. The inlay is positioned over the line of sight using a sophisticated alignment system. The Kamra is implanted into one eye only and this is the eye that then enjoys the enhanced near vision. The distance vision remains very good. The procedure is also completely reversible: for anyone who does not like the result, the inlay can be removed.
Kamra Inlay with a small central opening that helps focus vision for reading.
The Inlay is much smaller and thinner than a contact lens.
How does the Kamra work?
The KAMRA inlay is an implant designed to reverse the effects of presbyopia and restore near and intermediate vision by using small aperture optics, the same principle used in a pinhole camera.
When inserted in the cornea the dark ring of the Kamra inlay serves to block out unfocused light while the small opening in the centre of the inlay allows focussed light to reach the retina. This means that vision is enhanced at all distances looking at a movie screen, working on a computer, and also reading text on a cellular phone.
With focused light rays, you can enjoy a wider range of improved vision for all distances near, far and in between. The small-aperture technology is a superior alternative to options that use a multi-focal approach.
What are the Advantages of the Kamra inlay
The KAMRA inlay is designed to improve functional near vision and reduce dependency on reading glasses. Although eliminating the need for reading glasses typically occurs, you may occasionally need reading glasses for reading in dim light, or reading very small print. The Kamra inlay offers effortless natural vision, and by having the inlay implanted there are significant advantages over reading glasses or contact lenses.
| Reading Glasses | Kamra Inlay |
| Easy to misplace | An implant that offers unparalleled ease and convenience. |
| Blur distance vision | Brings near objects into focus. Distance vision remains virtually unchanged. |
| Visible indicator of aging/vision loss | So small it is nearly impossible for others to see. |
| Not ideal for all | No lenses that smudge or fog up. |
| activities/conditions. | No bulky glasses that limit activities. |
| Contact Lenses | Kamra Inlay |
| May be hard to position and/or easy to lose. | No need to reposition or struggle with the inlay. It won’t move or fall out. |
| Ongoing replacement and upkeep cost. | Hassle-free, long-term benefits after being implanted in one eye. |
| Not for long-term or overnight use. | Safe and effective long-term solution for improving near vision. |
| Only improves vision if worn. | Works continuously. |
| LASIK & Cataract Surgery | Kamra Inlay |
| May diminish near vision. | Revives near vision even after these common procedures. |
Your First Step
Contact a KAMRA™ Inlay Specialist Today
If you’re ready to take the next step, the KAMRA™ inlay can take you on a journey of near vision rejuvenation. There’s nothing like the ease, convenience and clarity of this remarkable inlay. So, why wait? Get started today
Every doctor listed on our site is trained to examine your eye health and history and determine if this technology is right for you. It’s time to feel more confident and in control. Just imagine taking back the freedom to enjoy your everyday activities without having to reach for your reading glasses. That’s the power of change and the power of the KAMRA inlay. Natural vision for everyday living.
Eye Gymnasium
-
Gymnasium with a difference
-
you have to visit us only once in 6 weeks
-
Eye exercise to be done at any convenient time of the day
-
Eye Exercise in the comfort of your home
-
Computer based diagnosis and Exercise too